How to write Naive Bayes classification algorithm in Ruby
Let's look at some real problems that can be solved with this solution:
- decide which comment is positive or negative
- deciding which email is OK or spam
- sentiment analysis
- recommendation algorithm for products, movies
- fraud detection by determining the probability that a given transaction is a fraud based on transaction characteristics and payment history
How the algorithm works
The Bayesian algorithm uses this relationship to calculate the probability of a class given a set of features, and then chooses the class with the highest probability as the classification for the item. The algorithm can be used for various classification tasks, including spam filtering, sentiment analysis and text classification.
Here's a brief overview of the Bayes algorithm process:
- Collect a set of data that you want to classify. This data should be labelled, meaning that each piece of data has an associated category or class.
- Split the data into two sets: one for training and one for testing. The training set will be used to train the algorithm, while the test set will be used to evaluate the accuracy of the algorithm.
- Calculate the probability of each class based on the frequency of occurrence in the training set. This is known as the prior probability and is used in the Bayesian computation.
- Calculate the probability of each feature (e.g. a word in a document) given each class. This is the probability of observing a feature given a class and is calculated by dividing the number of times the feature appears in a class by the total number of features in that class.
- Use the prior probability and the probability to calculate the posterior probability of each class given a feature. The posterior probability represents the probability of a class given the features of a test item.
- Use the posterior probabilities to classify the test items by choosing the class with the highest probability.
- Evaluate the accuracy of the algorithm by comparing the predicted classes to the actual classes of the test items.
Note that this is a simplified overview of the Bayes algorithm, and there are various variations and nuances of the algorithm depending on the specific use case and implementation.
Sample implementation in Ruby
Let's provide a simple implementation of a categorization analysis - for example, detect email category (spam or OK) based on the title.
class LineParser
def self.call(text)
text.gsub(/[^0-9A-Za-z\s]/, '').downcase.strip
end
end
class DataLoader
attr_reader :data, :categories
def initialize
@data = Hash.new { |h, k| h[k] = Hash.new(0) }
@categories = []
end
def add(text)
text.split("\n").each do |line|
words = LineParser.call(line).split
category = words.shift
@categories << category
words.each do |word|
@data[category][word] += 1
end
end
@categories.uniq!
end
end
class CategorizerAnalysis
attr_reader :categories, :test, :group_a, :group_b, :normalization_factor, :data
def initialize(test, data_loader)
@test = LineParser.call(test)
@data = data_loader.data
@categories = data_loader.categories
@group_a = 1.0
@group_b = 1.0
@normalization_factor = 1.0
end
def analyze
test_words = @test.split
total_words_size = (@data[@categories.first].values.sum + @data[@categories.last].values.sum).to_f
test_words.each do |word|
words_count_in_each_category = (@data[@categories.first][word] + @data[@categories.last][word]).to_f
words_count_in_each_category = 1 if words_count_in_each_category == 0
@normalization_factor *= words_count_in_each_category / total_words_size
@group_a *= (@data[@categories.first][word] + 1).to_f / @data[@categories.first].values.sum.to_f
@group_b *= (@data[@categories.last][word] + 1).to_f / @data[@categories.last].values.sum.to_f
end
total_answers = (@data[@categories.first].size + @data[@categories.last].size)
@group_a *= @data[@categories.first].size.to_f / total_answers
@group_b *= @data[@categories.last].size.to_f / total_answers
output
end
private
def output
{ @categories.first => @group_a / @normalization_factor,
@categories.last => @group_b / @normalization_factor,
}.tap do |output|
output[:winner] = output[@categories.first] > output[@categories.last] ? @categories.first : @categories.last
end
end
endLineParser is a simple class that takes the text as input and returns the processed text, stripping all non-alphanumeric characters and whitespace, converting the text to lower case, and stripping any leading or trailing whitespace.DataLoader a class that allows you to add and store data in a hash. The data consists of categories and words, and for each category the frequency of each word is stored. It also keeps a list of unique categories. It's easy to modify this class to retrieve and store the data in the database rather than in-memory.CategorizerAnalysis is a class that uses the sample data from the DataLoader class and the test line to perform a categorization analysis. The class performs a Naive Bayes analysis by calculating the probability of each category given the test data and normalizing the results. The class outputs a hash containing the probability of each category and the winning category, i.e. the category with the highest probability factor.
So, the algorithm is not difficult to understand. But let's see the results in practice. First, we need to provide some data to 'train'.
data = "OK Meeting reminder: Discussion on Project Proposal
OK Invitation to attend the company's annual conference
OK Action Required: Approval of T&E expenses
OK Important update on HR policies
OK New product launch: Introduction to Oxycon
OK Weekly update: [CEO] progress report
OK Follow-up on our recent call regarding our expenses
OK Reminder: Deadline for the project
OK Happy birthday! Kamil
OK Opportunity for career growth: Oxycon is hiring
SPAM Congratulations You won a free trip
SPAM Get rich quick with this secret investment opportunity
SPAM Limited time offer Huge discount on prescription drugs
SPAM Unclaimed inheritance waiting for you
SPAM Confirm your account information now
SPAM You're a winner in our latest sweepstakes
SPAM Important information regarding your bank account
SPAM Increase your penis size
SPAM Unlock the secrets to unlimited wealth
SPAM Congratulations! You've been selected for a free grant"Next is to load the data into CategorizerAnalysis and run it!
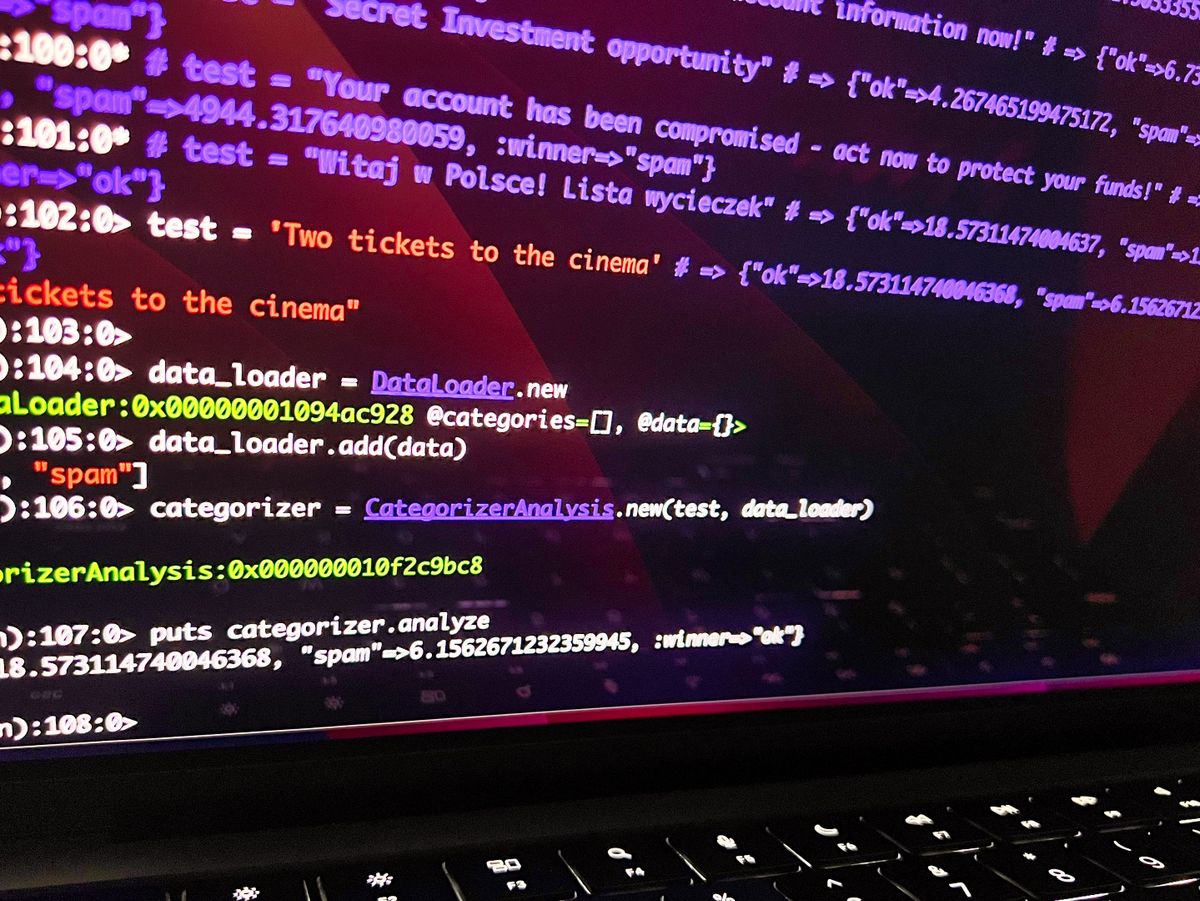
test = 'Two tickets to the cinema'
data_loader = DataLoader.new
data_loader.add(data)
categorizer = CategorizerAnalysis.new('', data_loader)
puts categorizer.analyzeLet's test the results for these sample email titles.
test = "Email about recruitment process from our company" # => {"ok"=>80.83500978270477, "spam"=>34.064212755592656, :winner=>"ok"}
test = "You won" # => {"ok"=>1.0227809155766943, "spam"=>5.865253212396069, :winner=>"spam"}
test = "Contract to sign" # => {"ok"=>4.267465199475173, "spam"=>2.503335586243119, :winner=>"ok"}
test = "Urgent: Confirm your bank account information now!" # => {"ok"=>6.7362508152254, "spam"=>1226.3116592013364, :winner=>"spam"}
test = "Secret Investment opportunity" # => {"ok"=>4.267465199475172, "spam"=>15.020013517458713, :winner=>"spam"}
test = "Your account has been compromised - act now to protect your funds!" # => {"ok"=>85.06609506965489, "spam"=>4944.317640980059, :winner=>"spam"}
test = "Witaj w Polsce! Lista wycieczek" # => {"ok"=>18.57311474004637, "spam"=>13.851601027280989, :winner=>"ok"}
test = 'Two tickets to the cinema' # => {"ok"=>18.573114740046368, "spam"=>6.1562671232359945, :winner=>"ok"}I was shocked at how correctly it was categorized and the proportions between them. The results look pretty cool compared to the simplicity of the algorithm. I highly recommend it for simple things.
Full gist can be found here.
Happy coding!